


Digital Circuit & System

Beschreibung von Digital Circuit & System
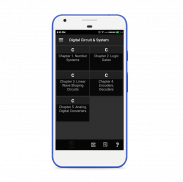
It is swipe based design for electrical & electronics student to learn digital circuit & system .It almost cover all topics which are given below chapter wise
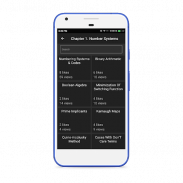
Chapter 1. Number Systems
1. Numbering Systems & codes
2. Binary arithmetic
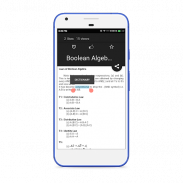
3. Boolean algebra
4. Minimization of switching function
5. Prime Implicants
6. Karnaugh Maps
7. Quine-McClusky method
8. Cases with don't care terms
Chapter 2. Logic Gates
1. Introduction to logic gates
2. Universal gate
3. Half adder
4. Full Adder
5. Half Subtractor
6. Full Subtractor
7. Series & parallel addition
8. Binary Coded Decimal adders
9. Carry Lookahead Adders
Chapter 3. Linear wave shaping circuits
1. Linear wave shaping circuits
2. Bistable
3. Monostable & Astable multivibrator
4. Schmitt trigger circuits & Schmitt-Nand gates
5. Logic families
6. Gated flip-flops and gated multivibrator
7. Interfacing between TTL to MOS
Chapter 4. Encoders, Decoders
1. Decoder
2. Encoder
3. Multiplexer
4. Demultiplexer
5. Semiconductor memory
6. Introduction to Shift Registers
7. Counters
8. Synchronous & asynchronous counters
Chapter 5. Analog, Digital converters
1. Digital to analog converter
2. Analog to Digital converters
3. sample & hold circuits
4. V-F converter
</div> <div jsname="WJz9Hc" style="display:none">Es ist Swipe basiertes Design für Electrical & Electronics Schüler lernen digitalen Schaltung & System .Es fast decken alle Themen, die unter Kapitel weise gegeben sind
Kapitel 1. Zahlensysteme
1. Nummerierung Systeme & Codes
2. Binäre Arithmetik
3. Boolesche Algebra
4. Minimierung der Schaltfunktion
5. Primimplikanten
6. Karnaugh Karten
7. Quine-McClusky Verfahren
8. Fälle mit egal Begriffe
Kapitel 2. Logikgatter
1. Einführung in die Logikgatter
2. Universal-Gate
3. Halbaddierer
4. Volle Additionsmaschine
5. Halb Subtractor
6. Vollsubtrahierer
7. Series & parallele Zugabe
8. BCD-Addierer
9. Trag-Vorausschau-Addierer
Kapitel 3. Lineare Wellenformungsschaltungen
1. Lineare Wellenformungsschaltungen
2. Bistabile
3. Der monostabile Multivibrator & Astable
4. Schmitt-Trigger-Schaltungen & Schmitt-NAND-Gatter
5. Logikfamilien
6. Gated Flip-Flops und gated Multivibrator
7. Schnittstelle zwischen den MOS-TTL
Kapitel 4. Encoder, Decoder
1. Decoder
2. Encoder
3. Multiplexer
4. Demultiplexer
5. Halbleiterspeicher
6. Einführung in die Schieberegister
7. Die Zähler
8. Synchron & asynchrone Zähler
Kapitel 5. Analog, Digital-Wandlern
1. Digital-Analog-Wandler
2. Analog-Digital-Wandler
3. Sample & Hold-Schaltungen
4. V-F-Wandler</div> <div class="show-more-end">

























